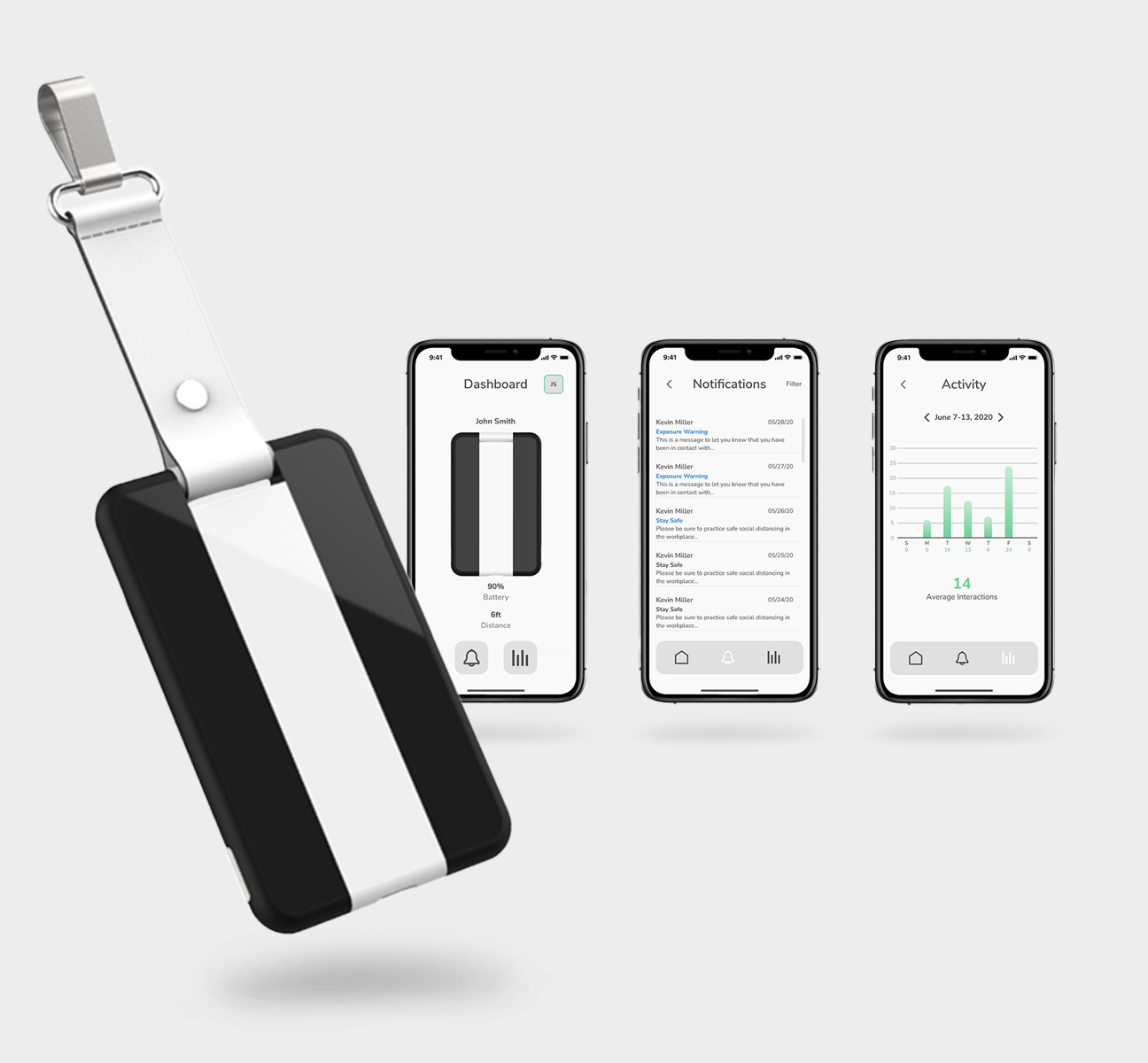
User-Centered Design
The success of a product depends greatly on its ability to satisfy user expectations, so at Acorn, we put end users and clients at the center of our decision-making and innovation. Our user-centered design process encompasses UX, ID, and UI in order to decipher insights, resolve pain points, and discover opportunities. By combining these core findings we can outline important criteria necessary to creating highly usable products and satisfying user experiences:
-
Conduct extensive user research to gain insights on target audience, understand the behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
-
Develop empathy to fully understand user perspectives and motivations.
-
Design an easy-to-use interface inclusive of users of all backgrounds.
-
Account for mistakes and take steps to reduce opportunities for confusion.
-
Organize every step of the user journey with logical and intuitive approaches.
-
Provide guidance to onboard and assist users as they accomplish their objectives and navigate through complexity.
-
Design to align with the target audience and market expectations, then break the boundary.
-
Provide consistent treatment throughout the platform to enhance familiarity and ease of use at every touch point.
-
Get user and market feedback and improve continuously.

UX Design
User Experience Design focuses on understanding the user’s needs, values, abilities, and limitations. Owning these valuable insights will elevate the product’s usefulness and the user’s desire by creating new opportunities. Extensive research and user testing can improve the quality of user interaction and perception of a product or service.
At Acorn a typical UX investigation produces descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analyses to set product requirements for the development phases. Our UX designers cohesively incorporate human factors, marketing, functionality, trends, risks, etc. into the research investigation.
Data Gathering & Synthesis
Human Factors Analysis
Descriptive Analysis
Predictive Analysis
Perspective Analysis
Industrial Design
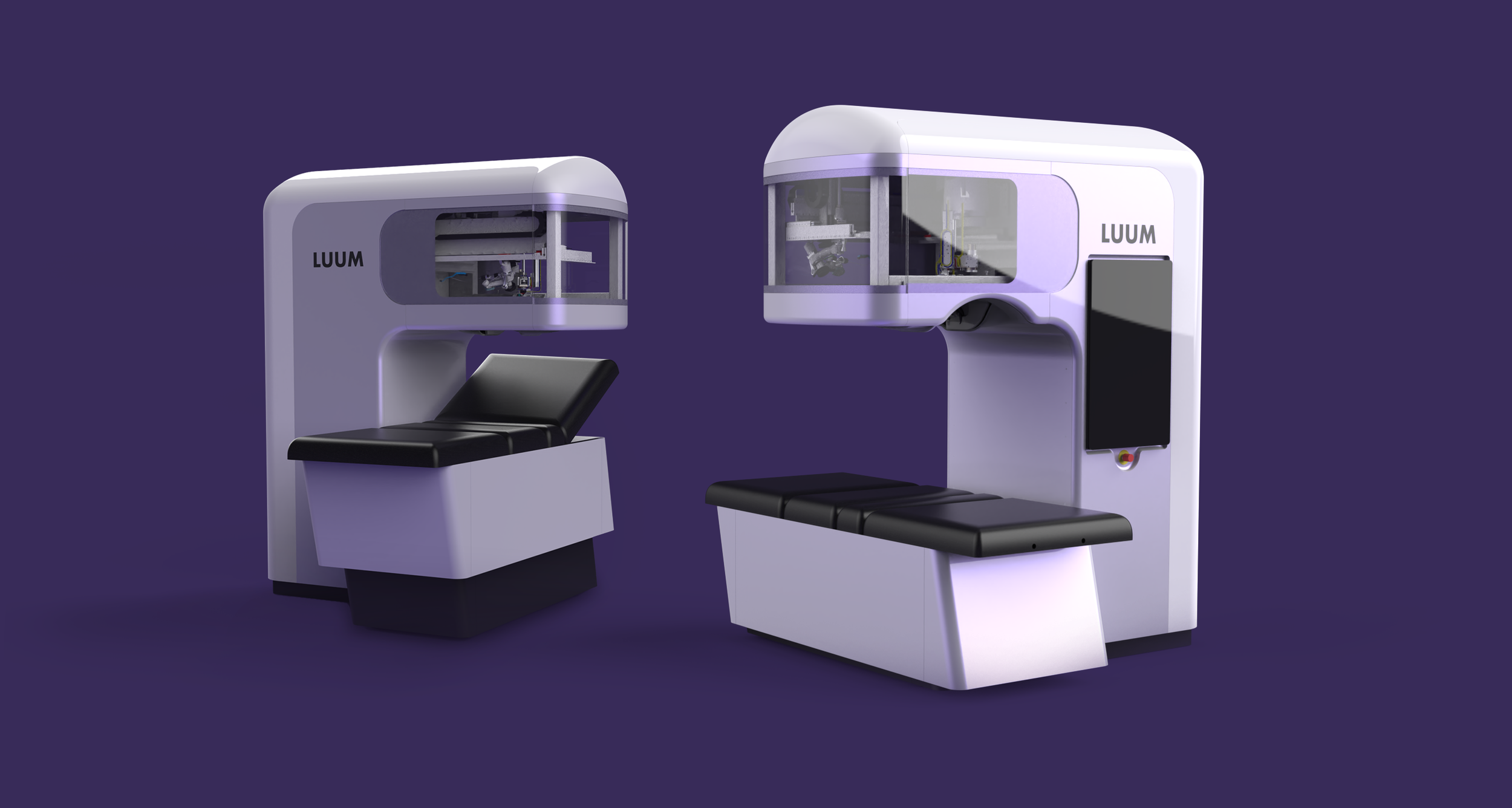
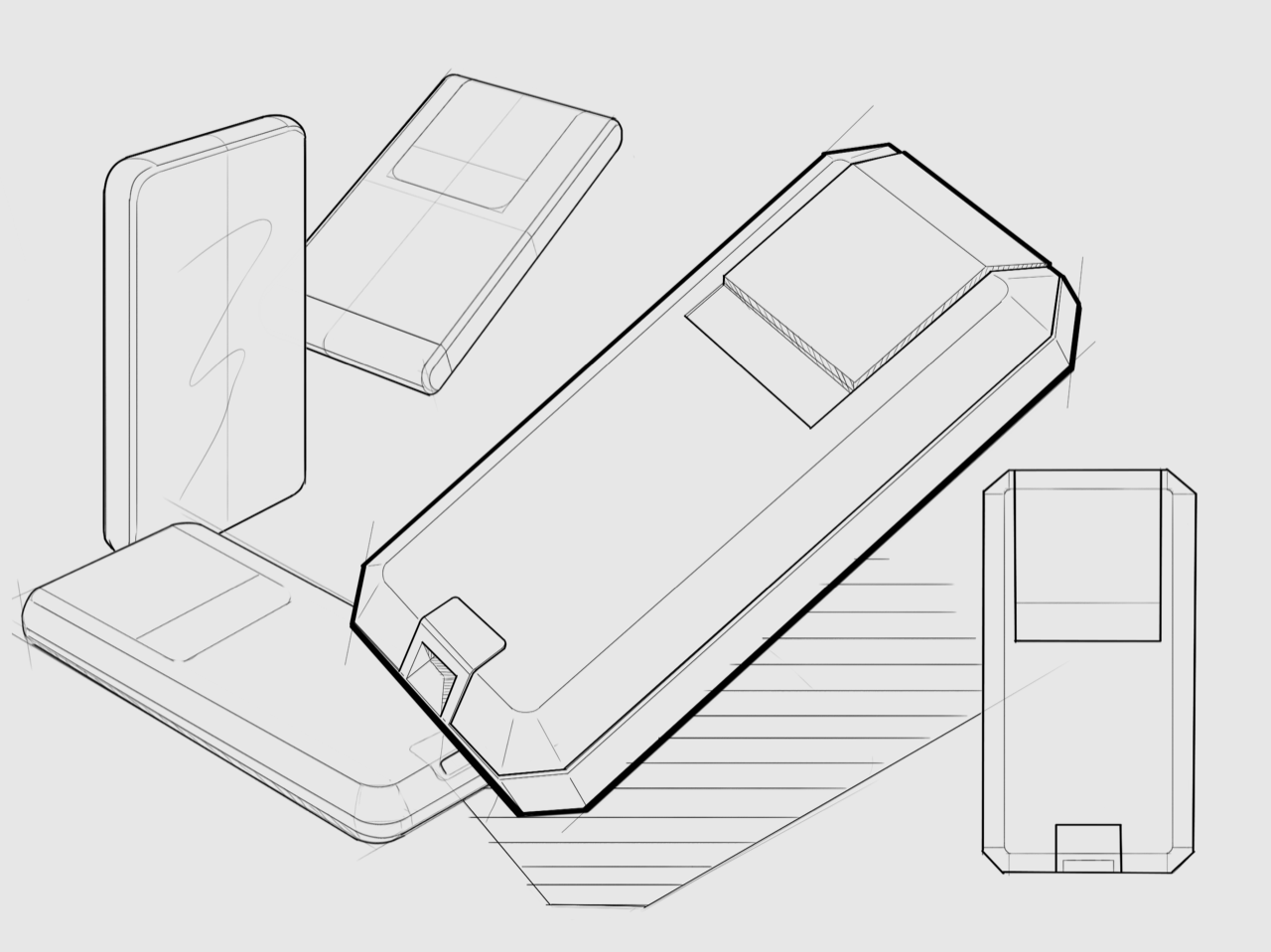
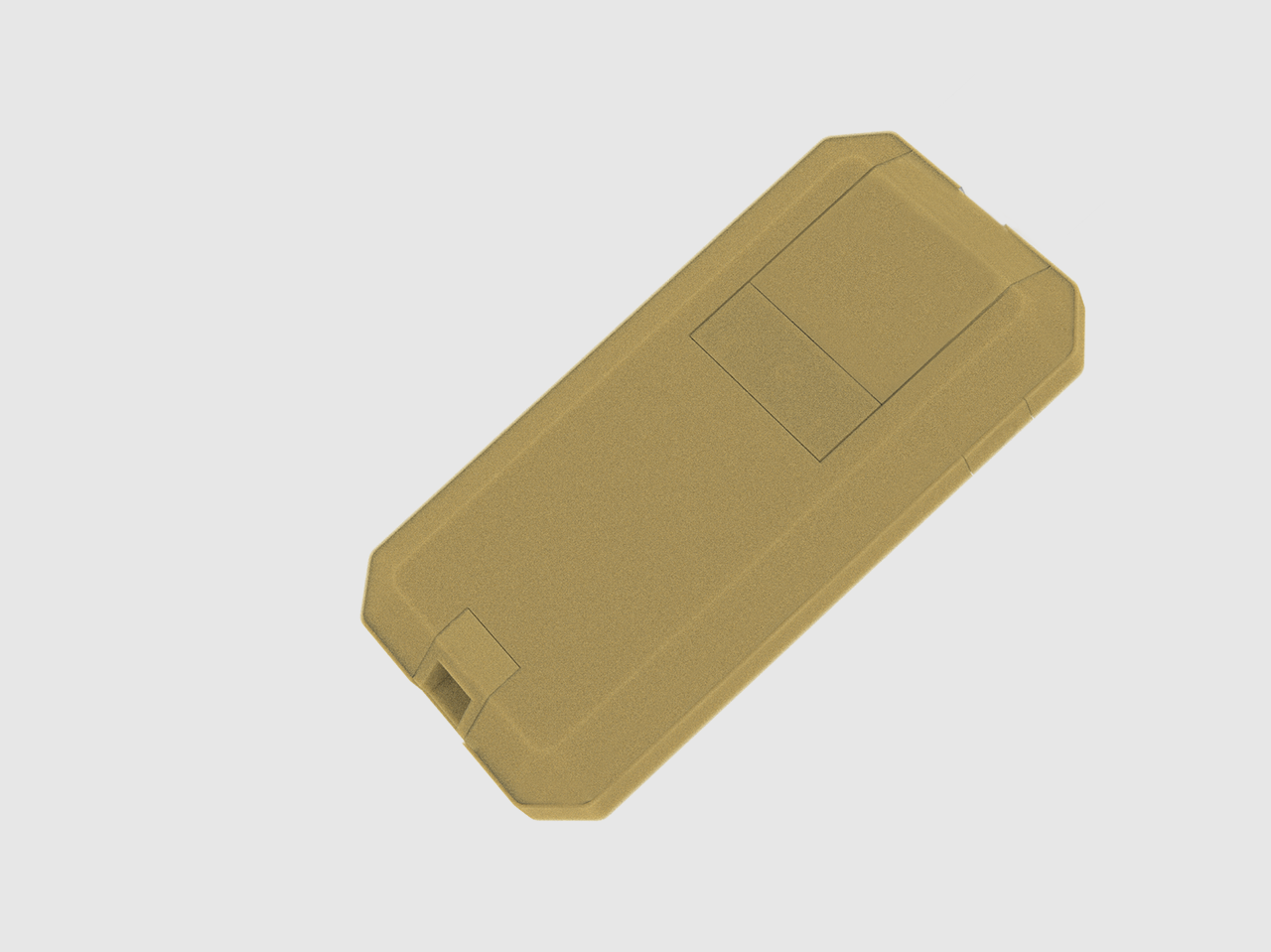
ID challenges the paradigm and explores possibilities for the purpose of creating value for the client’s product and brand. By incorporating UX, industrial designers become user advocates and deliver positive solutions.
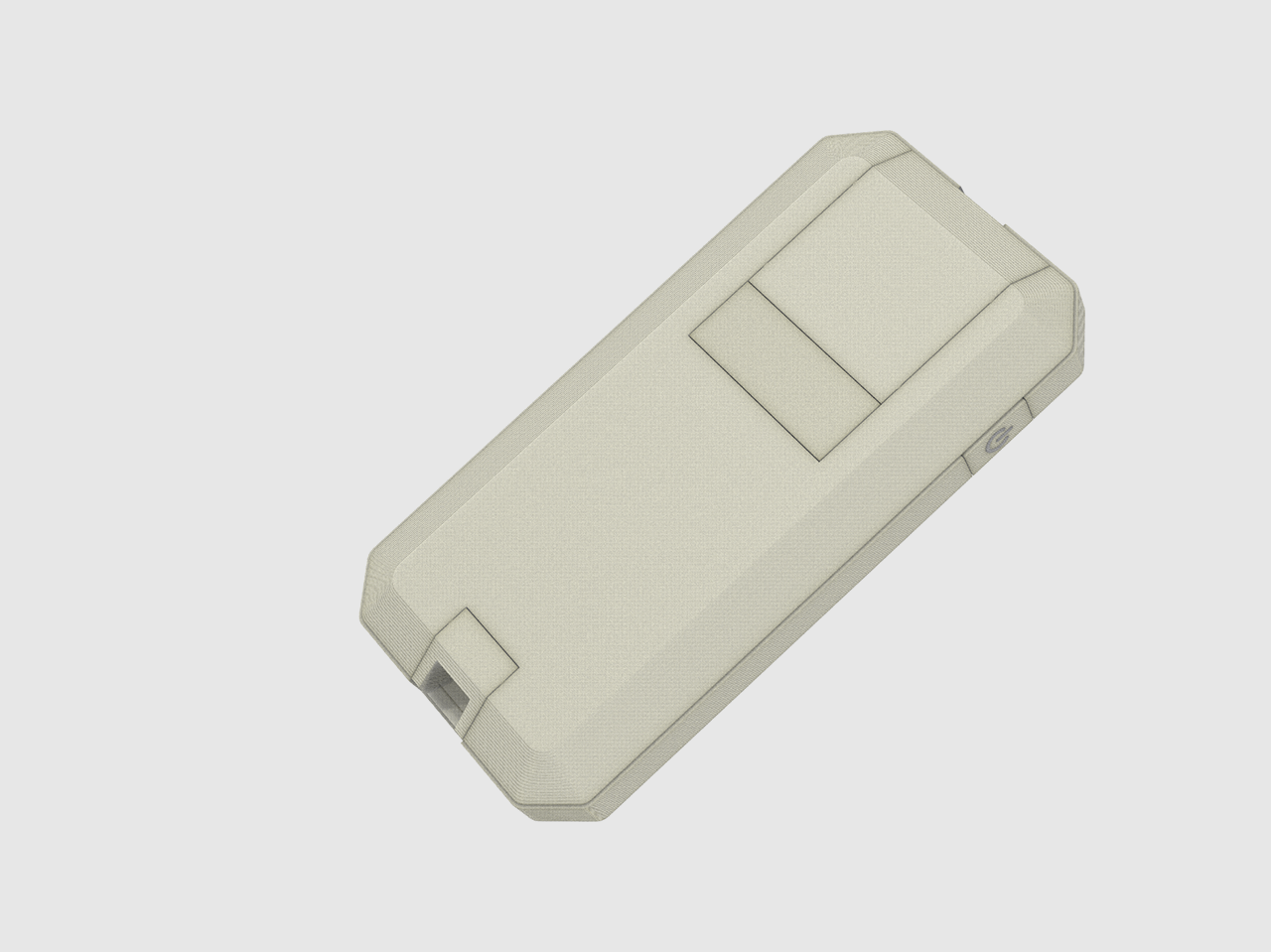
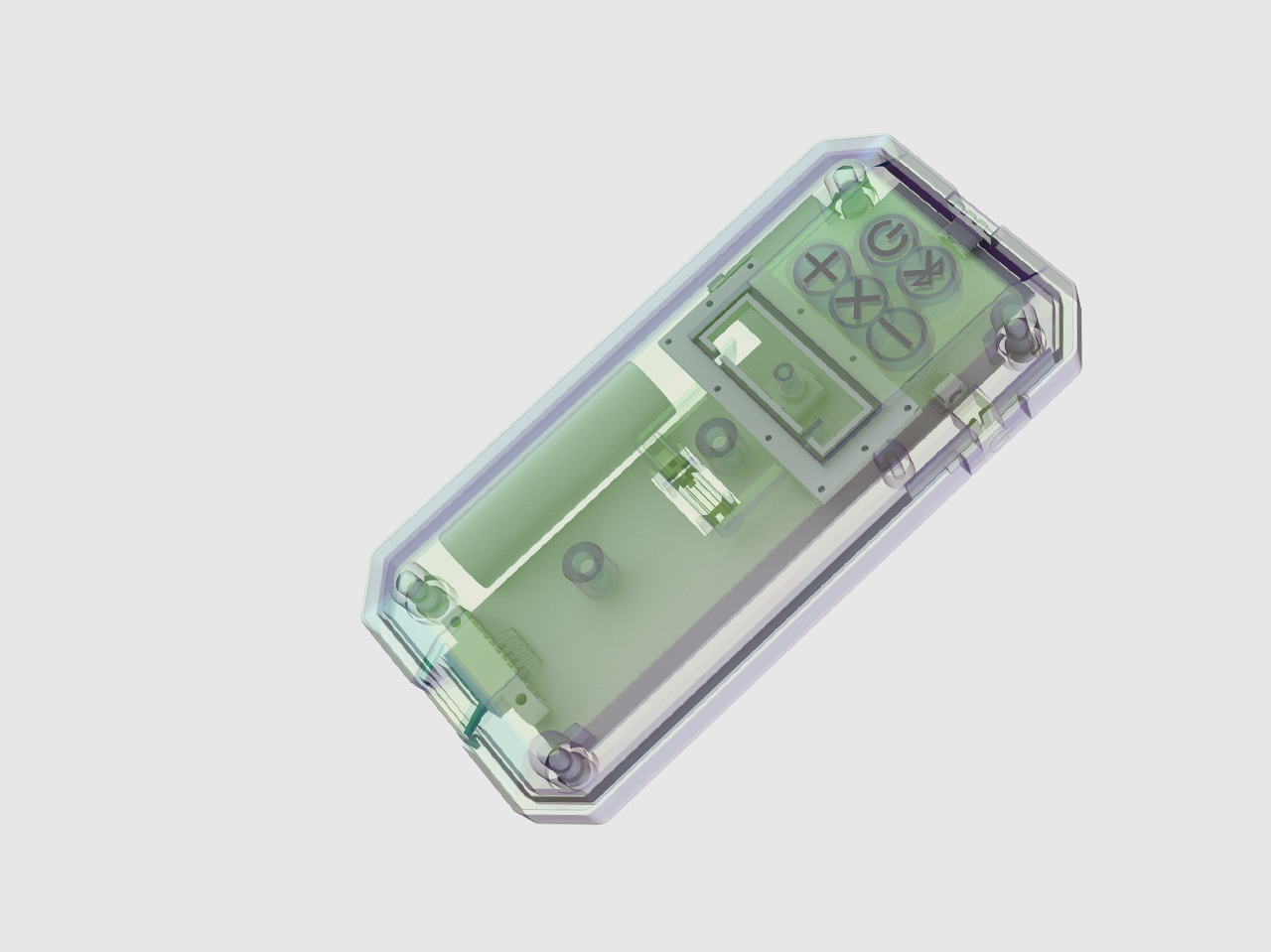
The ID process includes designing physical products, devices, objects, and services. The primary objective is to address a product’s physical aesthetics, functional features, and manufacturability. Designers must work closely with engineers to produce the highest quality product within the engineering, manufacturing, and marketing requirements throughout all phases of the development process.
Concept Development
Design Refinement
Prototyping & Testing
Product Refinement
UI Design
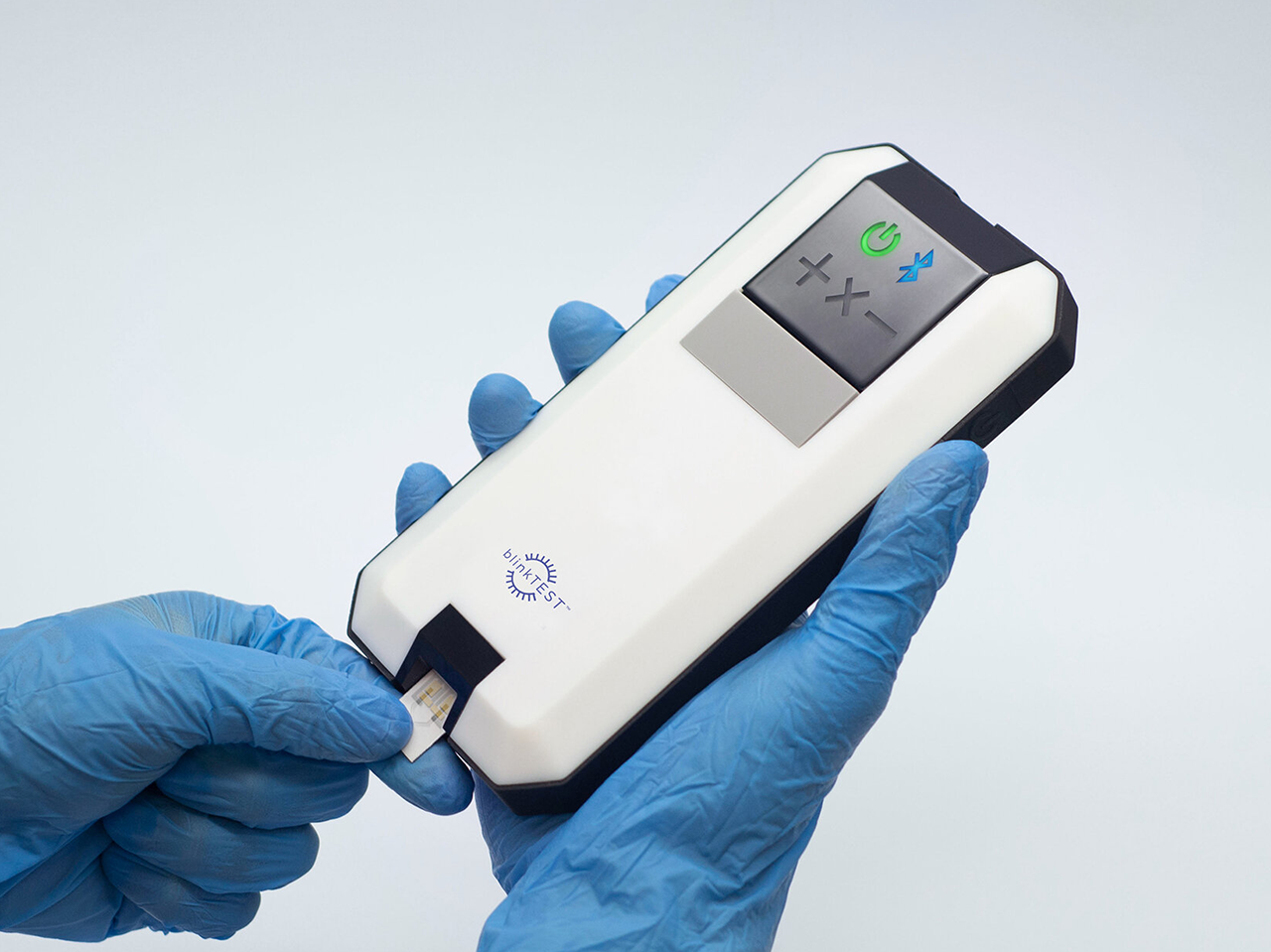
UI covers the design of interfaces and interactions in software and physical products. Examples of UI influences can be found in the graphic user interface of a smartphone or physical buttons of car interior panels. In both cases, the goal of UI is always to ensure the user can navigate and operate the product with ease and satisfaction.
UI design considers the architecture, navigation, and workflow of the product. Designers then build prototypes of the interface to ensure the user can complete the task with minimal effort. Lastly, the UI designer will work side-by-side with software developers to realize the product and deliver optimal usability and likeability.
Wireframing
Design Definition
Design Validation
Prototyping & Implementation
The Value of User-Centered Design
In today’s world of products and services, the bar to satisfy the customer has never been higher. Fierce competition across product spaces has not only increased the demand for quality but for the level of satisfaction expected from customers.
As product developers with almost 30 years in the industry, we recognize the standards to which users hold companies and their products as well as what it takes to meet them on the development end.
Schedule a free consultation today and see how User-Centered Design can make your project stand out!